At Happy Tails Animal Hospital in Renton, WA, under the esteemed leadership of Dr. Arshdeep Mann, we understand the discomfort and health issues pets face due to aural hematomas. This condition, often perplexing and painful for pets, necessitates prompt and knowledgeable care. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, management strategies, and prevention tips for aural hematomas, equipping pet owners with the knowledge to ensure their furry friends receive the best possible care.
Unveiling Aural Hematomas: Understanding the Basics
An aural hematoma is a blood collection within the ear flap, typically resulting from vigorous head shaking or ear scratching due to irritation. This condition can affect any pet but is more common in those with floppy ears or chronic ear infections. Recognizing the signs early can lead to quicker intervention and reduced discomfort for your pet.
Identifying the Causes
Several factors can prompt the onset of an aural hematoma in pets, including:
- Ear Infections: The most prevalent cause, leading to itching and subsequent trauma from scratching.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause ear irritation, prompting scratching and head shaking.
- Parasites: Ear mites and other parasites can lead to severe irritation.
- Trauma: Direct injury to the ear can result in a hematoma.
Symptoms to Watch For
Early detection is crucial. Symptoms include:
- Swelling of the ear flap
- Discomfort or pain when the ear is touched
- Head shaking or tilting
- Scratching at the affected ear
Expert Management at Happy Tails
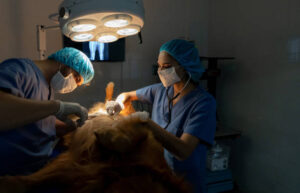
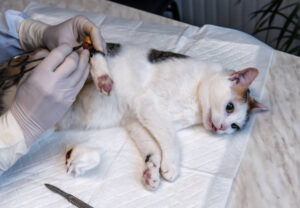
Dr. Mann and the team at Happy Tails Animal Hospital approach the treatment of aural hematomas with a combination of precision, compassion, and advanced veterinary practices. Treatment may involve:
- Aspiration: Draining the blood from the hematoma, though this method may see recurrences.
- Surgical Intervention: The most definitive treatment, involving draining the hematoma and suturing the ear to prevent refilling.
- Medication: Addressing the underlying cause, such as antibiotics for infections or medication for allergies.
The Recovery Process
Post-treatment, recovery is a critical phase where the pet’s comfort and healing are paramount. Happy Tails provides comprehensive aftercare instructions, including:
- Medication management to prevent infection and control pain
- Regular follow-up appointments for suture removal and check-ups
- Instructions on preventing trauma to the healing ear
Prevention: A Proactive Approach
Preventing aural hematomas involves addressing the root causes of ear irritation. Dr. Mann emphasizes the importance of regular exams and ear check-ups to catch and treat ear infections and parasites early. Additional preventive measures include:
- Maintaining regular ear cleaning routines, especially for pets prone to ear infections
- Monitoring for signs of allergies and seeking veterinary care for management
- Ensuring your pet’s environment is free from irritants that could lead to ear scratching
Partnering with Pet Owners for Optimal Ear Health
At Happy Tails Animal Hospital, we believe in a partnership approach to pet healthcare. Educating pet owners on the signs, treatments, and preventive measures for conditions like aural hematomas is key to ensuring the well-being of every pet. Dr. Mann and his team are dedicated to providing the resources, care, and support needed to manage pet health effectively.
For more information on aural hematoma treatment or to schedule an ear health exam for your pet, contact Happy Tails Animal Hospital at 425-254-2779. Together, we can ensure a comfortable and healthy life for your cherished companion.
Sources:
- Journal of Small Animal Practice: Offers insights into the latest treatment methods and success rates for aural hematomas in pets.
- American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA): Provides guidelines on ear care for pets, helping to prevent conditions that lead to hematomas.
- Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice: Features in-depth articles on the causes and management of ear diseases in pets, including preventive strategies for aural hematomas.